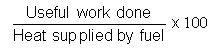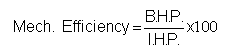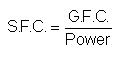Clearance volume – cross section area above the piston head when the piston is at top dead center.
Total volume – cross section area above the piston head when piston is at bottom dead center.
Swept volume – cross section area swept by the piston when it travels from top dead center to bottom dead center.
Compression ratio = Total Volume ÷ Clearance Volume
—————————————————————————–
Mechanical efficiency – of an engine is determination of the heat supplied to the engine as compared to the heat used in the useful work by the engine. Since we know some heat is dissipated by the accessories, gearbox and engine to run itself, the horse power produced by the engine (Indicated horse power) is compared to the horse power available to useful work(Brake horse power), which is always less than I.H.P, to find out the useful work done by the engine.
Therefore Mechanical Efficiency = B.H.P ÷ I.H.P. *100
—————————————————————————–
Propeller Efficiency – is calculate by the Thrust horse power produced by the propeller as compared to the Brake horse power available to the propel
Propeller Efficiency = T.H.P ÷ B.H.P.
—————————————————————————–
Airframe Efficiency – is the determination of airframe to produce lift at varying speeds, and produce least drag.
Airframe Efficiency = TRUE AIR SPEED ÷ DRAG
—————————————————————————–
Finess Ratio – is the ratio of a aerofoil fineness from chord to the thickness of the aerofoil.
Finess Ratio = CHORD ÷ THICKNESS
—————————————————————————–
THRUST SPECIFIC FUEL CONSUMPTION – is the thrust produced for a given amount of burnt fuel.
THRUST SPECIFIC FUEL CONSUMPTION = Weight of Fuel Consumed ÷ Lbs of Thrust
—————————————————————————–
Gross Thrust = momentum of outgoing gases.
Net Thrust = momentum of outgoing gases – momentum of incoming gases
Magnetos – when breaker points open the flow of current in the primary winding is arrested, the magnetic field around the primary winding collapses falling inward on itself and cutting the secondary winding.
Impulse Coupling – Momentarily rotates the magnetos to assist spark
—————————————————————————–
OAT usually over reads temperature (show more than actual) because the air passing through the a/c body gets heated due to the air friction.
Example – OAT over reads upto 10C at speeds of 90kls. and 40c at speed of around 200 kts and 300 c at 500 kts. Therefore, true air temperature can be calculated approximately by OAT.
—————————————————————————–
Tachometer shows the speed of engine crankshaft in hundreds of rpm. On fixed pitch propeller tachometer shows rpm of engine crankshaft and propeller, if the Propeller is not fitted with the reduction gearing.
For every one Power Stroke the Crankshaft rotates twice, therefore in a four stroke engine, four strokes are used to produce two revolutions of the Crankshaft.
In a Four Stroke Engine, producing maximum rpm of 2500 rpm Example- In Cessna 152, whose maximum rpm is near 2500 rpm, the no. of Power strokes occurring in a minute is 1250 or the number of total Strokes in a minute is 5000.
In a Constant speed propeller unit, Propeller rpm is on tachometer and Engine Power setting on manifold press gauge.
Manifold pressure gauge indicates pressure of fuel/air mixture in the engine intake manifold in inches of mercury. 14.7 psi is equal to 29.92 hg. Therefore, a manifold reading of 26” Hg indicates a pressure of about 13 pounds per squire inches (Psi).
Dead Cut Check – is done at low rpm to check continuity of the Magneto circuit.
Magnetos Drop Check – is done at high rpm to check Maximum drop of Magnetos (Magnetos Serviceability Check) & also to check Grounding wire of each Magnetos.
—————————————————————————–
Performance of Piston Engine
Specific Fuel consumption is ratio between weight of fuel consumed/ hour to power B.H.P.
Specific Fuel Consumption = weight of fuel consumed ÷ hour÷ B.H.P
If S.F.C is less it is best.
S.F.C. can be decreased by-
- Decreasing Fuel Consumption
- Increasing Brake Horse Power
- 1. Mixture Control
Rich Mixture – 8:1
Lean Min – 15: 1
Rich mixture gives better cooling of Engine and increases F.C. Lean mixture decreases F.C.
Lean min decreases F.C., Engine runs at higher Temperature, therefore it increases Thermal Efficiency of the Engine. Therefore we should use lean mixture during Cruise
- RPM and MAP
High MAP and low RPM is the best combination.
Advantage of low RPM:-
(i) Frictional losses decrease i.e. F.H.P. decreases.
(ii) Less power is used by engine accessory.
(iii) Less Super charger losses.
High MAP gives rise to better Volume Efficiency.
High MAP means that highest value of MAP that can be sustained with the lean mixture.
When using Above 70% power use Rich mixture.
3.Altitude – Altitude increases, pressure decreases, therefore MAP decreases.
Weight of Fuel Air mixture going inside the Engine decreases, therefore power output of the Engine decreases.
Normally Aspirated Engine is one not fitted with Super Charger it gives maximum power only at sea level.
– Rated power or Max continuous Power– Power can be maintained continuously without any restriction of time.
– At sea level to maintain rated power throttle will be less than maximum.
– Rated Altitude – Altitude up to which a normally aspirated engine can maintain its sea level rater power.
– Full Throttle Height – Altitude at which TBV is fully open for a selected value of MAP and RPM.
– Rated Altitude is the full throttle ht for the rated power.
– Lesser the power selected higher is the full throttle height.
Aircraft should be flown at rated Altitude for best S.F.C.
Because
(a) Throttle butter fly valve is fully open and engine is operating at its max efficiency.
(b) Outside pressure is less (Back pressure is less) therefore engine exerts less useful power to vent out the burnt gases.
Therefore B.H.P. increases.
(c) At rated Altitude due to colder Temperature, thermal efficiency is better.
- Temperature – Colder Temperature gives better thermal efficiency of engine.
- Carburettor Heat – Increasing the power output (RPM/MAP)
- Super Charger – Super charger device which increases pressure of fuel/ air mixture and maintains sea level rated horse power at on Altitude above the Rated Altitude.
It has Impeller which increases velocity, decreasing pressure and Diffuser decreasing velocity, increasing pressure.
Super charger has following characteristic:-
- It is engine driver at an RPM proportional to engine rpm.
(Its rpm is 8-10 times more than engine rpm.)
- At a given rpm, it can increase pressure by a fixed amount. It is generally available in 2 gears.
At low Altitude because pressure is already high, if we use super charger the pressure will increase further and detonation may take place. (Due to hot air entering the Carburettor)
Therefore to prevent this to happen we have ABC.
ABC (Automatic Boost Control)– It helps to maintain the MAP and prevents detonation at a low Altitude.
ABC has a capsule, which gets input from MAP. When MAP increases, ABC capsule contracts, TBV decreases and MAP decreases.
As Altitude increases ABC capsule expands and opens TBV.
At the rated Altitude TBV is fully open.
(Just like Altitude capsule at sea level contracts)
Critical Altitude– Critical Altitude is Altitude up to which a super charged engine (Turbo charged) can maintain its sea level rated horse power.
At low Altitude we use super charger in low gear because increasing pressure requirement is less- pressure is already high.
At high Altitude we use supercharger in high gear because increasing pressure requirement is more- pressure is low at high Altitude.
We climb above the Critical Altitude with low gear let MAP drop by 1”-2” and then change to high gear.
Modern super charger engine is 2 stage super charger. At low Altitude we use 1 stage. At high Altitude we use both stages.
1st stage is between Carburettor and Induction Manifold.
2nd stage is before the Carburettor.
– Rated Altitude – Altitude at which normally aspirated engine can maintain its sea level Rated H.P.
– Critical Altitude – Altitude at which a super charged (Turbo charged) engine can maintain its sea level rated horsepower.
Above Critical Altitude engine power decreases.
- Turbo Charger– Turbo charger is an exhaust driven super charger. It is driven by the exhaust gases.
Heat energy is obtained by burning of fuel/ air mixture.
40% of heat is Converted to Mechanical energy.
30% Heats engine and parts.
30% goes out as exhaust.
This 30% going out as exhaust is used to run turbo charger.
Therefore it increases the Thermal efficiency of engine.
Since it does not use any engine power to run, it decreases S.F.C.
Whereas a super charger increasing S.F.C. because it uses engine power to run impellor and diffuser.
A turbo charges is run by exhaust gases of engine.
When waste gate is fully closed all the gasses go over the turbine wheels they will start rotating and in turn will rotate compressor which increases pressure and therefore increasing MAP.
Waste gate is closed using oil.
Waste gate is opened by spring pressure.
Increase in oil press closes it and spring tension opens waste gate.
When waste gate is fully closed, there is max power and vice-versa.
In a turbo charged engine waste gate controls detonation at low Altitude.
On ground when engine is off, waste gate is fully open.
On starting engine and engine idling waste gate is fully closed.
At sea level for T/o when you open throttle fully waste gate fully opens.
– As Aircraft climbs waste gate slowly starts closing.
– At Critical Altitude waste gate is fully closed.
– For every one Power stroke there are two revolutions.
– If cylinder of a 4 stroke engine fires 200 times a minutes. The crankshaft will have 400 rpm.
– After firing is caused by excessively rich mixture.
– Tappet clearance is measured between volume stem & Rocker Pad.
– Blue Smoke – is due to Oil burning.
– Black Smoke – is due to Rich Mixture.
For every one Power stroke, Four Cycles take place.
One power stroke occurs in a four Cycle, but Crankshaft rotates twice.
Camshaft rotates at half the speed of Crankshaft.
Swept volume – Volume of cylinder swept by the Piston in one stroke.
Clearance Volume – Volume area between Cylinder head and Piston head, when Piston is at Top Dead Centre.
Total Volume = Swept Volume + Clearance Volume.
Work = Force x dist.
Power = Force x dist. / Time
For Engine Horse Power
PLANK ÷ 33,000
P – Mean effective pressure in lbs²/inches in the Cylinder.
L – Length of stroke in feet.
A – Area of Cross section in the Cylinder
N – No. of power strokes every minute
K – No. of cylinders in engine.
Piston engine/Constant Volume cycle – Ignition takes place at constant volume.
Thermal Efficiency – is ratio between useful work done by the engine to the heat supplied by fuel
Volumetric Efficiency – is the ratio between weight of fuel/air mixture drawn in the engine to the weight of fuel drawn in standard condition of Temperature & Pressure theoretically.
Detonation can lead to Pre-ignition, but not vice versa
METO – Maximum Except Take off Power = Maximum Continuous Power = Rated Power.
Rated Altitude – is that altitude, at which throttle butterfly value is fully open for a given value of MAP & RPM.
As altitude increases outside pressure decreases therefore engine has to exert less power to vent out exhaust gases therefore Frictional Horse Power decreases & Brake Horse Power increases.
At high altitude, Thermal efficiency increases BHP increases and therefore Specific Fuel Consumption will improve.
In a fixed pitch Propeller, on applying Carburetor heat the presence of icing is indicated by a drop in rpm.
In a Constant speed Propeller, on applying Carburetor heat the presence of icing is indicated by a drop in Manifold Absolute Pressure.
Critical Altitude is the Altitude, up to which a super charged engine can maintain its sea-level rated horse power.
Throttle Controls – AIR flow.
Thrust lever controls – Fuel flow.
Up draft Carburetor – in this carburetor air flows from down to up.
For Carburetor icing to occur, certain conditions are required as follows-
1) Visible Moisture in air
2) Range of temperature for icing is +20oC to -10oC.
In Dual Magneto system – everything is duplicated except rotating magnetos.
If on checking magneto drop, no drop is observed the grounding wire is broken.
For checking Right Magneto-
Ignition is turned from Both to Left No Drop, Right magneto grounding wire is broken.
For checking Left Magneto-
Ignition is turned from Both to Right No Drop, Left magneto grounding wire is broken
A Dead cut check is done to check magnetos and to check the continuity of the Electric circuit, it is usually done at low rpm.
Oxidation occurs when Hot oil exposed to oxygen, the oil loses it’s lubricating properties & hence change of oil is required
—————————————————————————–
PISTON ENGINE
Stroke – is a movement of piston from one dead centre to the other dead centre.
Clearance volume – is the volume of cylinder & the piston head when piston is at Top Dead Centre.
Swept volume – is the volume of cylinder traveled by the piston in one stroke.
Swept volume & clearance volume = Total Volume OR
It is the volume of cylinder area above the piston when piston is at Bottom Dead Centre.
Compression Ratio is the ratio between Total volume to Clearance volume
Greater the compression Ratio greater is power output
Mechanical Efficiency is ratio between Brake Horse Power to Indicated Horse Power & is expressed in % age.
Thermal efficiency is the ratio between useful work done by the engine to the heat supplied by the burning of fuel.
For a 4 stroke cycle crank shaft rotates twice, therefore for 2400 rpm there are 1200 power strokes.
Volumetric Efficiency – is ratio between weight of fuel/air mixture drawn inside the engine to the weight of fuel/air mixture drawn inside the engine under standard conditions of temperature & pressure theoretically.
Note – Volume Efficiency is a ratio of weight & not of volume.
If Specific Fuel Consumption is less, Engine is more efficient.
Engine efficiency depends upon Specific Fuel Consumption.
Rated Altitude is the altitude, at which a normally aspirated engine can maintain its sea level rated horse power.
The A/c should fly at the Rated Altitude, because the throttle butterfly value is fully open & engine is operating at it’s maximum efficiency.
Full Throttle Altitude is altitude at which throttle butterfly value is fully open for a given below of MAP & RPM.
Lower the power selected higher is the Full throttle height.
Critical Altitude is the altitude at which a Super Charged engine can mention its sea level rated horse power.
In cold temperature the thermal efficiency of engine improves.
Super charger maintains Rated power at high altitude.
At low altitude, low speed (gear) of the supercharger is used.
At high altitude, high speed (gear) of the supercharger is used.
With super charger Specific Fuel Consumption increases.
We cannot have MAP above sea level pressure.
Pressure above atmospheric pressure is called positive boost.
Pressure below atmospheric pressure is called negative boost.
Ground boosted supercharger can give MAP more than sea level pressure.
Turbocharger – is an exhaust gases driven Super charger.
It increases Thermal efficiency & decreases Specific Fuel Consumption.
Waste gate controls Turbo charger.
Waste gate closes turbine speed increases and rpm increases.
Waste gate opens turbine speed decreases & rpm decreases.
Waste gate helps prevent detonation at low altitude by opening the waste gate.
Waste gate opens by the spring force.
Waste gate closes by the oil pressure.
When engine is off, the waste gate is fully open.
When Engine is on idle conditions, the waste gate is fully closed, sensing low pressure in the MAP.
At sea level on Take off, waste gate is fully open.
As altitude increases, waste gate slowly closes.
At Critical Altitude, waste gate is fully closed.
Boost pressure gauge shows pressure in induction manifold in lbs per inches above or below the atmospheric pressure.
Boost Positive means 1 lb above atmospheric pressure.
Boost Negative means 1 lb below atmospheric pressure.
Spark plug fowling – is due to low RPM & Rich Mixture.
Overprime – Engine is over-rich with mixture.
Tickler/Primer – is provided to make engine easier to start by pumping fuel into the carburetor.
Blue smoke – is due to Oil burning
Black Smoke – is due to Rich Mixture